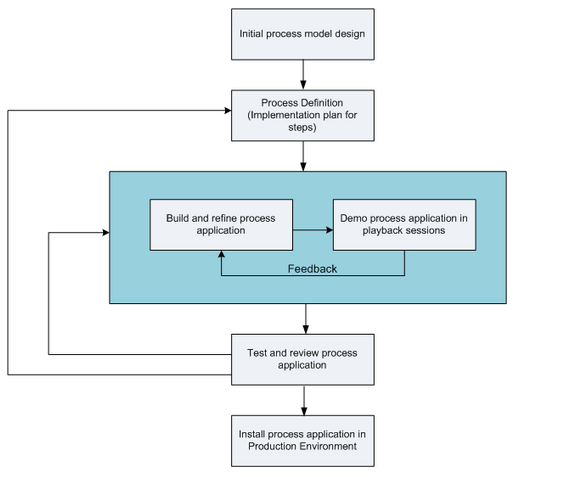
The following diagram shows the life cycle of a typical process development effort. It includes steps for building and refining an installation service so that you can install your process applications in the production environment.
As this diagram shows, you can work exclusively in your development environment. But you need to configure Process Servers for both your test and production environments.
- Overview of process modeling
A process is the major unit of logic in IBM Business Process Manager. It is the container for all components of a process definition, including services, activities and gateways; timer, message, and exception events; sequence lines, rules, and variables. When you model a process, you are creating a reusable Business Process Definition (BPD). - Process development with the Process Center
IBM Process Center serves as a central repository for all project assets created in Process Designer. When multiple Process Designer clients connect to the Process Center, users can share items, such as processes and services, and can also see changes made by other users as they happen. The Process Center can also be used as a repository for assets created in IBM Integration Designer. - Process applications: Overview
A process application is a container for process models and their supporting implementations; it is stored in the repository. After the artifacts have been authored or otherwise created, they are assembled into a process application and a snapshot is taken. You can test, install, and administer the process application snapshot. - Running and debugging processes
Using the Inspector, individual developers can run processes and services on the Process Center Server or remote runtime Process Server. - Deploying and managing process applications
The process application life cycle includes deploying and undeploying snapshots and managing snapshot states. Versioning considerations are also part of the lifecycle.
For training on IBM Lombardi BPM latest version mail us at [email protected]

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed