For training on IBM Lombardi mail us at [email protected]
|
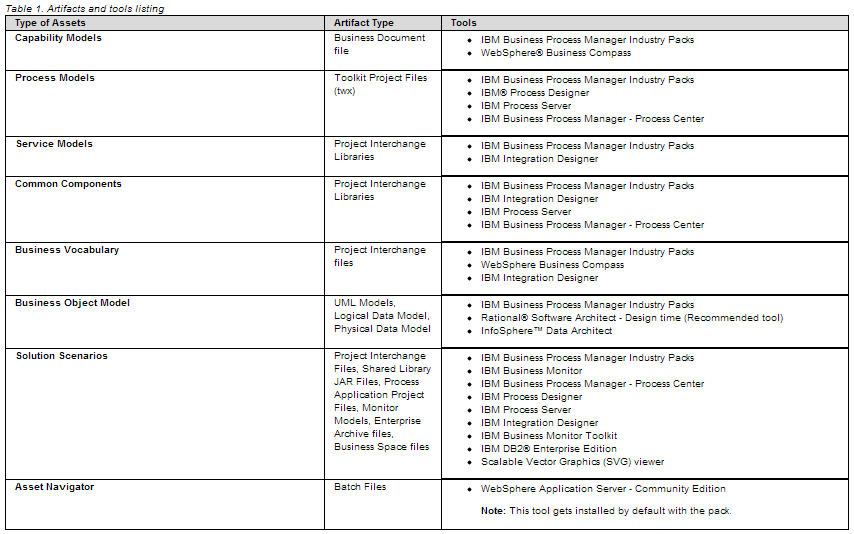
The development tools are required for working with the Business Process Manager Industry Packs and the BPM solution developed using the Business Process Manager Industry Packs assets. Note: Before using any of these tools, ensure that you have the latest fix packs and interim fixes.
For training on IBM Lombardi mail us at [email protected]
0 Comments
Accessibility features help users with physical disabilities, such as restricted mobility or limited vision, to use information technology products successfully.
IBM strives to provide products with usable access for everyone, regardless of age or ability. Use assistive technologies, such as screen-reader software and digital speech synthesizer, to use what is displayed on the screen. Consult the product documentation of the assistive technology for details on using those technologies with this product. You can operate features using the keyboard instead of the mouse. you can customize display attributes such as color, contrast, and font size. You can magnify information presented in the graphical views for more detail. A U.S. Section 508 Voluntary Product Accessibility Template (VPAT) can be requested on the IBM web site at http://www.ibm.com/able/product_accessibility/index.html. The information center documentation includes the following additional features to aid accessibility:
For training on IBM Lombardi mail us at [email protected] How we can do the FT and LB enable in configuration.xml (i.e. other than the Admin Console)
Update the field “IsFT” to ‘true’ in configuration.xml to enable Fault Tolerance Update the field “IsFT” to ‘false’ in configuration.xml to enable Load Balancing. How to enable logging of information for all activities in a project to be deployed in Administrator? In admin console go to running instance—>select tracing—> configure tracing –> check the “All Activities” checkbox enable—> then save Note: Administrator must have super user privileges in the UNIX box to perform this action. How to make the configuration changes available permanently for an application ? In <Application>.tra do the changes in bwengine.tra file also. Usually for each deployment the <Application>.tra wash out and replace with new one with default values. To restart a Admin domain we must follow the following shutdown and startup procedure Shut Down ?
How to extend the validity of the self signed certificate by another 2 years? Make use of keytool provided by Java to increase validity of self signed certificates Command: “keytool -selfcert -v -alias server -validity 730 -keystore teststore.jks -storepass mypassword”. How to find list of ports currently used by other applications? netstat –an How to handle following error message displayed in Tibco Administrator Error message: “No matching software for service archive Process Archive. The service is disabled”? Process Archive was deployed in a machine the Business Works runtime engine has not been installed. Make sure Business Works Engine is installed on the machine where PAR file is going to be deployed. Notes: You can add Tibco Active Matrix Business works machine using “Add to additional machines” option in Tibco Administrator. Process archive is showing “Need to deploy in a Service Container” error message. Make sure EAR file contains all the required resource during EAR file creation Maximum no of process that can be loaded into memory can be set using? By Using Max Jobs at .Par level Advanced Tab in Tibco Admin. How to modify GV after .ear file is deployed ? By adding property in the Application.tra file ( But not recommended) What are the two fault tolerance options supported by Tibco admin.? Fail Back and Fail over What is the Global variable used for pointing the certificate location? %%BW_GLOBAL_TRUSTED_CA_STORE%% Is it advisable to store certificate in more than one GV? NO When ever Tibco administrator configuration is corrupted how to get it back. Need to restore it back to last successful configuration date. When we make some changes in the global variables of any adapters deployed on a server and trying to redeploy it again faced some issues like On admin GUI at deployed configuration we see Server plugin failed. What needs to be done in such scenarios? When we try to do the same we can see server plugin failed for whatever the updates we does for the adapter. So here we need to bounce/stop and restart the administrator domain on which we have deployed the adapter and even have to bounce the Hawk agent on that Server. When we are trying to deploy an EAR file on Administrator sometimes we may face an issue deploying it. For these kinds of scenarios mostly we will be bouncing the Administrator and Hawk agent. This may/may not work sometimes. In case it doesn’t work we need to remove/delete the temp files created (if windows we can find them in .TIBCO directory in C drive, if it is unix server we can see them in \usr\tmp directory) and restart the administrator. If i deployed a process with HTTP receiver on 4 machines in FT mode. The client application doesn’t have any idea about on which IP machine the process instance is running. How you will make sure the client application request will go appropriate machine where process instance is running? IP redirector If your application is already deployed and running. Application has adapters and BW processes. If any changes are done in adapters and redeployment is required without affecting BW process. How adapter changes can be deployed without affecting BW process. When changes are done in adapter and need to deploy. Do not check in on Force deployment option. This way only adapter will be redeployed and BW will not be affected. What is the advantage of scripted deployment in Tibco and how it differs with normal deployment? Below are the scenario: 1. Whenever the TIBCO Administrator is down we have to deploy application from TRA -> Appmanage. 2. In case we have to deploy various applications using same global parameters, we have to provide every time these parameters in TIBCO administrator wile deployment. In such case its better to get a best practice to deploy application from backend using the scripts. Below are the advantages: 1. If Admin is down we are able to deploy application 2. We use a properties file (XML) which is having all the variables which can be used by various similar Applications. Hence, similar domain can be created fast. For training on TIBCO Administrator mail us at [email protected] IBM Business Process Manager Advanced: Process Server offers two authoring environments. Use IBM Process Designer to efficiently model business processes that involve human tasks. Use IBM Integration Designer to build services that are self-contained or that invoke other existing services such as web services, enterprise resource applications, or applications running in CICS and IMS.
Process Designer is available in all editions of the product. IBM Business Process Manager Advanced: Process Server also offers Integration Designer with its associated editors and adapters. Process Designer A process is the major unit of logic in IBM Business Process Manager. It is the container for all components of a process definition, including services, activities and gateways; timer, message, and exception events; sequence lines, rules, and variables. When you model a process, you are creating a reusable business process definition (BPD). Use IBM Process Designer to create process models that can contain human tasks. Process Designer helps you develop business processes. With an easy-to-use graphics-oriented tool, you can create a sequence of actions that compose a business process, and you can redraw that process over time as circumstances change. If one or more activities require access to large backend systems or services that provide data for the business process, for example to get information on customers, you can meet that need using Integration Designer. Using a simple interface, an activity in Process Designer can call a service created in Integration Designer. That service can use mediation flows to transform, route, and enhance data and adapters to get to many backend systems in standard way. In short, Process Designer focuses on the business process and Integration Designerfocuses on automated services to complement the business process. All Process Designer projects are contained in process applications. You store those process applications and associated artifacts in the Process Center repository. Process applications can share assets that have been placed in toolkits. IBM Business Process Manager provides several user interfaces to enable you to model, implement, simulate, and inspect business processes. You create and manage process applications, toolkits, tracks, and snapshots in the Process Center Console. You can create process models, reports, and simple services in Process Designer. You can run and debug processes in the Inspector. And you can run simulations in the Optimizer. Processes applications developed in Process Designer can at any time be run on the Process Center server or saved to a snapshot and deployed on the Process Server. The same is true of services developed in Integration Designer and associated with process applications. Integration Designer Integration Designer provides editors and aids to help developers create complex automated processes and services. It is available as a component in IBM Business Process Manager Advanced or as a stand-alone toolset for other uses. IBM Integration Designer has been designed as a complete integration development environment for those building integrated applications. Integrated applications are not simple. They can call applications on Enterprise Information Systems (EIS), involve business processes across departments or enterprises, and invoke applications locally or remotely written in a variety of languages and running on a variety of operating systems. The components are created and assembled into other integrated applications (that is, applications created from a set of components) through visual editors. The visual editors present a layer of abstraction between the components and their implementations. A developer using the tools can assemble an integrated application without detailed knowledge of the underlying implementation of each component. Integration Designer tools are based on a service-oriented architecture. Components are services and an integrated application involving many components is also a service. The services created comply to the leading, industry-wide standards. BPEL processes, which also become components, are similarly created with easy-to-use visual tools that comply to the industry-standard Business Process Execution Language. In the Integration Designer paradigm, components are assembled in modules. Imports and exports are used to share data between modules. Artifacts placed in a library can be shared among modules. Modules and libraries can be associated with a process application for use with the Process Center and can be used as services by processes created in Process Designer. In such cases, they can also be deployed with the process application. Alternatively, modules and libraries can be deployed directly to the test environment or to the Process Server. You can use mediation modules to create mediation flows, which you can deploy to WebSphere Enterprise Service Bus or to the Process Server. IBM Integration Designer also provides the capability for creating data types and xml maps that can be deployed on the WebSphere DataPower appliance. You can also transfer files to and from WebSphere DataPower. For training on IBM Lombardi mail us at [email protected] When you introduce a new version of a BPEL process, you might want this version to apply to both new process instances and to instances that have already started. This can be important in environments where changes to processes are needed frequently, but where an individual process instance can be relatively long-lived. In such cases you need to migrate the process instances that are running to the newer version. You can create a new version of a BPEL process in one of the following ways:
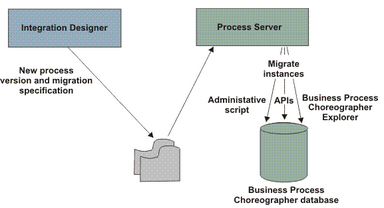
For example, the following figure shows the steps for defining a new version of the process in Integration Designer through to migrating running instances in Process Server. In general, for a new version of a BPEL process to become a migration target, you must deploy a migration specification together with the new version of the process. If you deploy a new snapshot of a process application or toolkit with the same BPEL process implementation as a previously deployed snapshot, the new version the BPEL process automatically becomes a migration target for the previously deployed snapshot.
To migrate running process instances to a new version of the process, you can use either an administrative script to migrate process instances in bulk, or Business Process Choreographer Explorer to migrate specific instances.When migration is triggered, the process, the variables, and the activities that are at the current position of the process navigation now refer to the new version of the BPEL process and the follow-on navigation depends on the logic of the new version of the BPEL process. The activities that have already been navigated when the process instance is migrated are not migrated. During the migration of a process instance, all the instances of inline human tasks, which belong to this process instance and are not yet in an end state, are also migrated. If the changes to the process that are contained in the new version of the process do not affect the process logic, such as the display name or description of an activity, a running process instance can be migrated any time during the process navigation. However, if the changes affect the process logic, such as new activities, variables, or conditional expressions are changed, you can migrate a running process instance to a newer version only if all of the changes that affect the logic of the process are after the current position in the process navigation. For example, any change to an inline human task is considered to affect the logic of the process. You can migrate a running process instance to a newer version only if all of the changed inline human tasks are after the current position in the process navigation. If events are defined for the BPEL process, you can track process migration using Common Base Events (CBEs). An event can be generated when the migration is started and again when the migration is complete. A history of process migrations is also kept in the Business Process Choreographer database. Process migration exampleTo work through an example of process instance migration, go to the Business Process Management Samples and Tutorials web site.
For training on IBM Lombardi mail us at [email protected] |
Archives
March 2017
AuthorWrite something about yourself. No need to be fancy, just an overview. Categories
All
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed